Title: Intelligent water management model project in Samariang, Kuching, Sarawak
Period: July ~ October , 2024 (3 months)
Introduction
This case study presents the results of a comprehensive field survey conducted in Samariang, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia, as part of the “Intelligent Water Loss Management System in Sarawak, Malaysia” project funded by GGGI-BKCF. The project was led by WI.Plat, starting from March 18th, under the leadership of Sanghoon Cha, Seunghwan Jung, and their team members.
The primary objective of the project was to reduce Minimum Night Flow(MNF) by 20% so that local government of Sarawak can save producing cost of supplied water so more people living in Sarawak can reach to the safe and clean water.
Key activities included:
- Negotiation to implement the project between local Sarawak government, Korean government institute and WI.Plat
- Data acquisition from local government and analysis to plan a leak detection strategy with local investigation
- Establishment of intelligent water loss management system for technical transfer
- Capacity building with local government and local partner
- Finalize the leak points to recover and verify the project goal to reduce Minimum Night Flow by 20%
The project’s main goal and objective is to provide clean and safe water for those who are suffering from physical water loss that connects to not obtaining revenue(tariff) from customers and having difficulty in providing clean and safe water to customers who are residing outside the city due to low water pressure and lack of water flow.
In order to meet the main and objective, State-of-art data-based technology is established through 3rd call of GGGI-BKCF fund. Along with the technology, IoT devices, GIS web and mobile based software is applied for the project
The implementation of an intelligent water loss management in Samariang represents a significant step towards sustainable development and improved quality of life for its residents. By leveraging advanced technologies and data-driven approaches, this project aims to, reduce water losses to help reduce MNF figure, enhance water loss management without hiring highly experienced leak detection experts with expensive leak detection device and improve overall leak management system efficiency. The findings from this field survey will not only guide the development of tailored solutions for Samariang but may also serve as a valuable reference for similar initiatives in other communities facing water management challenges.
The following sections of this report will delve into the methodologies employed, present detailed findings from each area of investigation, and offer preliminary recommendations based on the observed conditions and collected data.
Description of the project methods
WI.Plat and local partner employed a comprehensive approach to detect water leak on the water management system in Samariang. The methodology encompassed both desk-based research and on-site outdoor activities, ensuring a thorough understanding of the current infrastructure and operational practices.
-
Establishing Relationships for Project Initiation
Building strong relationships with local government agencies is crucial for initiating the leak reduction project. The CEO of WI.Plat, who has worked extensively with K-Water (Korea Water Resources Corporation, a government agency under the Ministry of Environment in Korea), has leveraged his international experience to connect with government authorities. His connections helped facilitate the collaboration with MUT (Ministry of Utilities and Telecommunications).
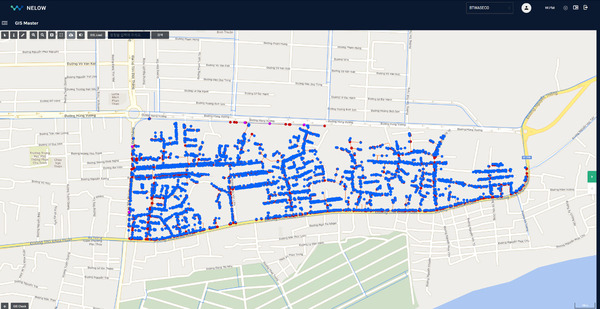
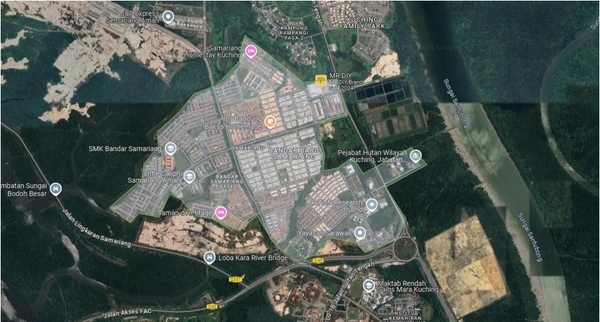
For the project, software utilizing AWS cloud services for the Malaysian region and manufacturing IoT devices were essential components. Prior to assessing the local site, GIS data was required. JBALB, the project’s beneficiary, provided GIS data for the Samariang area. This enabled WI.Plat’s civil engineers to understand the water pipe network in Samariang.
-
Acquiring Local Data for Building an Intelligent Leak Management System and Analyzing Local Characteristics
After signing a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) with the local government, GIS data and survey forms were requested and subsequently provided. These were analyzed to understand the local characteristics of the water pipeline network. A strategy for leak detection was developed, which included collecting leak sounds from households and identifying locations to install remote water pressure monitoring devices. EPANET software was also used to gain a comprehensive understanding of the geological characteristics, allowing engineers to pinpoint which parts of the site were most vulnerable to water leaks.
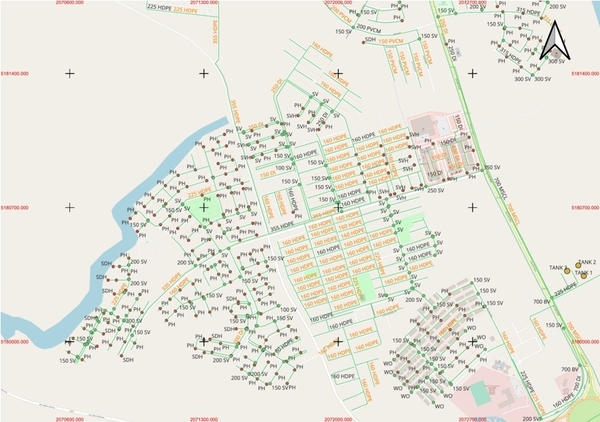
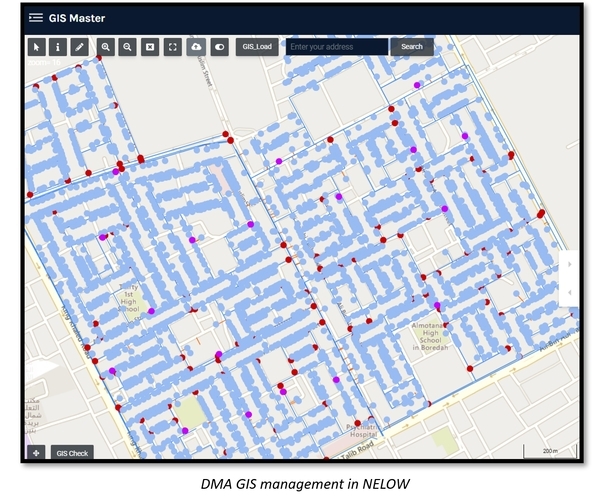
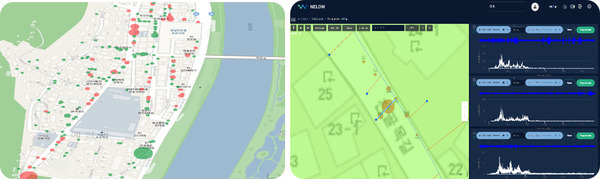
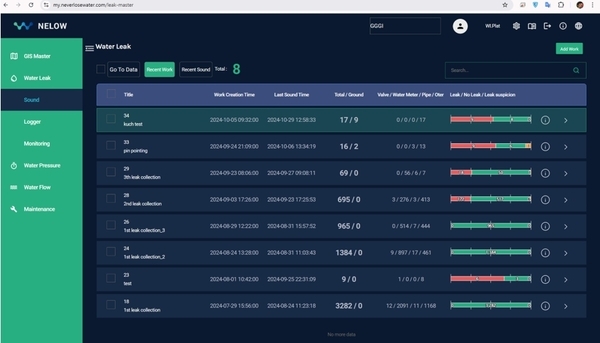
WI.Plat’s NELOW (NEver LOse Water) system, an intelligent water loss management system, was built on Amazon Web Services (AWS) in Malaysia using the GIS data. NELOW allows users to pinpoint the exact locations of water facilities, including water meters, valves, and pipes, offering a user-friendly interface for water management.
-
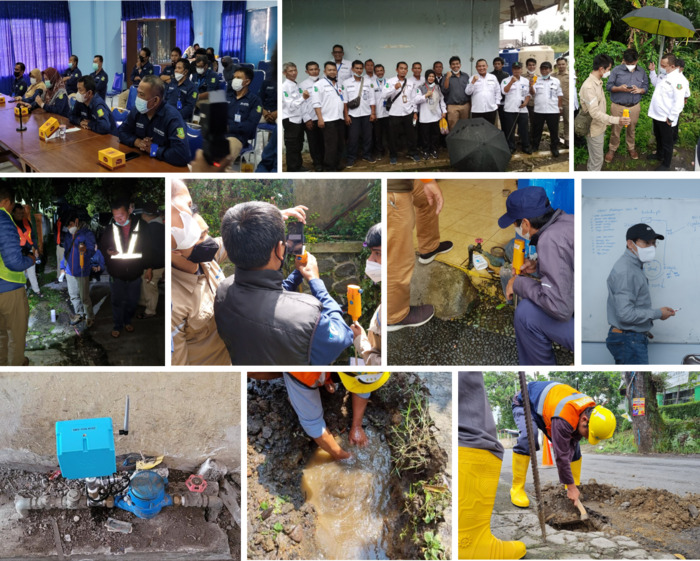
Technical Transfer and Capacity Building
Once NELOW was set up, technical transfer and capacity building commenced on-site. A two-year license was issued for each NELOW account, granting access to local water authority officers and partners. WI.Plat engineers made multiple site visits to train local staff on leak sound collection, remote monitoring device installation, and pinpointing leaks. This training ensures that local personnel can independently manage water loss, promoting the sustainability of the project.

-
Achieving Project Goals through Leak Detection and Recovery
With the IoT devices in place and data collected, both minor and significant leaks were detected. The project’s primary goal is to reduce the Minimum Night Flow (MNF), a key indicator of water loss during low-demand periods. The reduction in MNF will directly contribute to achieving the project’s water conservation goals.

Detailed On-site Activity Results
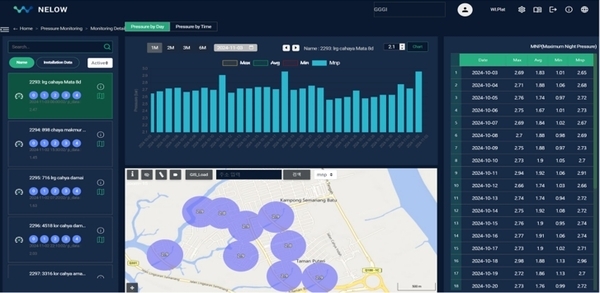
1. Summary of Facility Survey Results
The investigation of the water management system in Samariang area revealed a mix of strengths and areas requiring improvement.
- Water Distribution System (WDS): The WDS in Samariang delivers excellent service, providing consistent water pressure 24 hours a day. The average pressure of 2.5 bar over a 24-hour period is deemed satisfactory. The primary source of raw water is heavy rainfall, supplemented by a smaller portion of groundwater. Although there is an abundant water supply, concerns remain regarding water conservation due to climate change and the use of groundwater, which increases the risk of seawater intrusion, especially in Samariang, which is close to the South China Sea. Additionally, the high Non-Revenue Water (NRW) rate remains a significant issue.
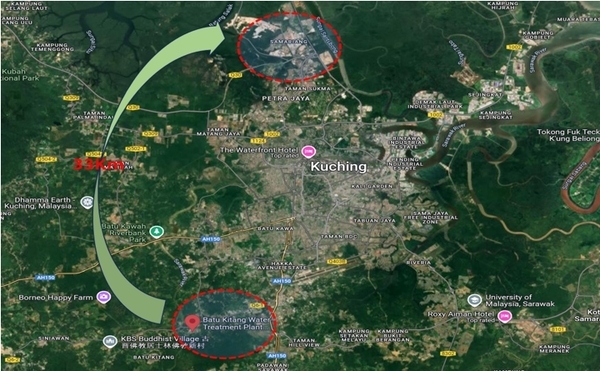
- Water Treatment Plants: Related Plants: In Samariang, raw water is primarily sourced from reservoirs formed by ample rainfall. The water drawn from these sources is processed at the Baku Kitang Water Treatment Plant (WTP) and then transported over 33 kilometers of pipelines to the booster pumps. This water is subsequently distributed to three tanks, supplying the entire Samariang area.

- NRW Management: The Non-Revenue Water (NRW) rate across Kuching city stands at 59%. Given that water is priced at 0.3 ringgit (approximately 0.1 US cents), this model could potentially lead to financial challenges. Consequently, the Sarawak state government is aiming to tackle water loss reduction by commissioning relevant services each year. This investigation revealed that the equipment used primarily consists of acoustic devices and multi-point, dual-point correlation leak detection products by Ovarro (formerly Primayer) from the UK. Although these products are high-end, they are reportedly difficult to operate, and pinpointing precise leak locations has proven challenging. As a result, the equipment has been stored away and remains unused.
- Metering and Billing: Water charges are currently determined by meter readers who visit each property with a water meter on a monthly basis to check usage. In the past, attempts were made to use smart metering for remote data acquisition, but issues with communication and facility management have resulted in the discontinuation of this practice.

- Water meters and Infrastructures: Water meters are installed in most residences, positioned around waist height for adult men, making it convenient for meter readers to check readings. Valves are well placed along each alley, and as there is no cold weather in the region, pipes are either buried approximately 1 meter deep or run above ground. For flow measurement, Siemens flow meters are installed at Main DMA and Sub-DMA inlet points, with data transmitted via Cello loggers for monitoring. This data is managed by the company partnered with the Ministry of Utilities and Telecommunications (MUT). Flow meters are also installed at schools and national facilities, ensuring robust monitoring of water flow


In conclusion, while the water supply system in Samariang exhibits some commendable features, significant improvements are needed in data management, operational guidelines, and water quality control to elevate the system to international standards. These enhancements will be essential for the successful implementation of an intelligent water management model in Samariang.
2. Detailed Leak inspection and detection Results
-
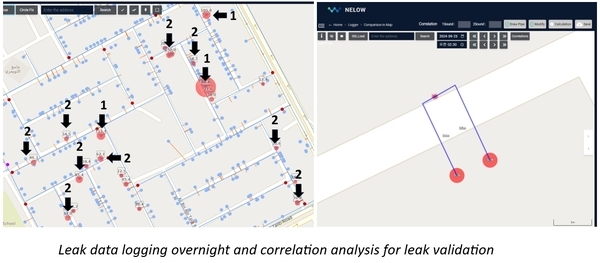
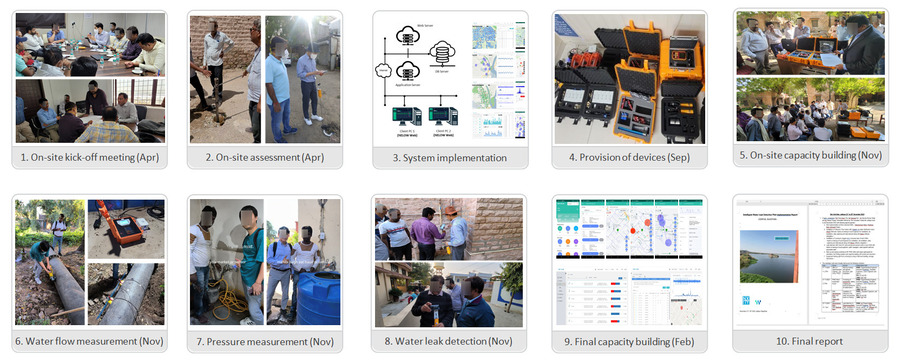
1st leak detection activity
Leak noise data collection began on July 29, during WiPlat’s visit to Kuching. At that time, GIS data for Samariang was provided, allowing us to begin data collection at points such as meters, valves, pipes, and hydrants based on this information. According to the GIS data, Samariang has 5,641 water meters, 153 valves, and a total pipeline length of 110.72 km. The data collection for leak noise was completed by August 31.
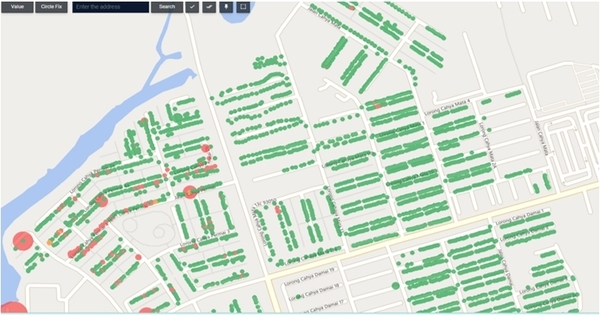

-
2nd leak detection activity
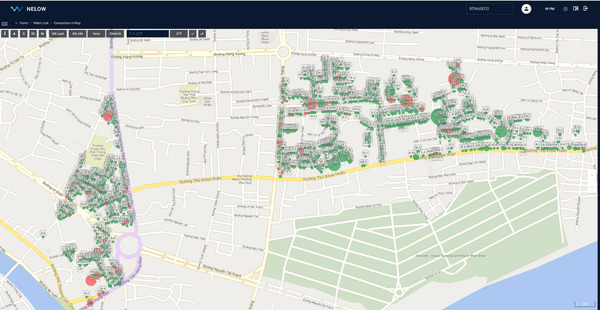
Based on the data collected in the first phase, a second round of noise collection was conducted in areas where high intensity signals were detected. While there were 695 instances in total, site engineers kept brief notes on conditions during data collection, allowing us to focus on the most suspicious areas. A notable finding during the second noise collection was the presence of considerable electrical noise. Common interferences included nearby barking dogs, passing vehicles, conversations, and sounds from meters in operation, as well as electric noise from utility poles. In this instance, the electrical noise originated from a pump near the meters, used to filter out excessive chlorine in the water supply. WiPlat, drawing on its experience in Korea, was able to distinguish electrical noise and gained insights into dealing with different types of pumps in future projects.
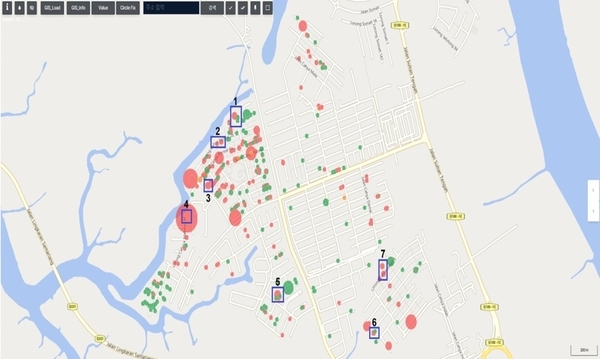
-
3rd leak detection activity with pin-pointing
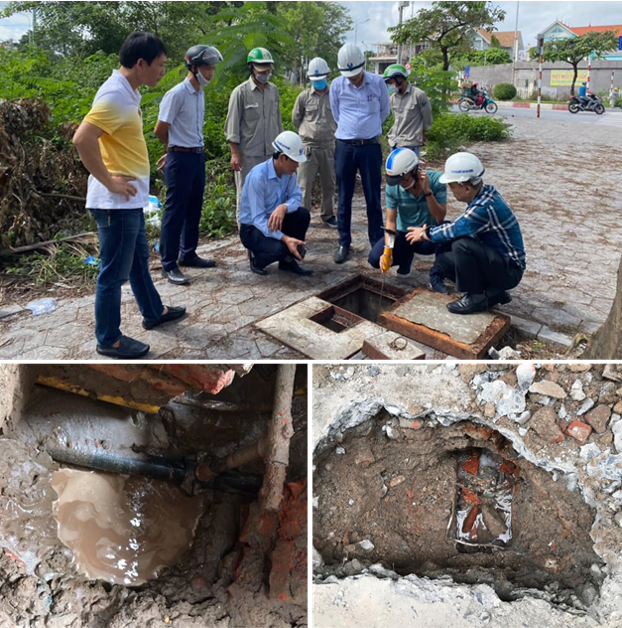
Using the results of the second round of data collection, six final suspected leak sites were identified. WiPlat returned to the site to conduct training on pin-pointing for surface leak detection and visited each of the suspected sites. Surface leak detection training was conducted in specific areas to enable precise identification of leak locations. In addition, visual inspections were performed, revealing visible leaks due to the site’s characteristics. At one site, a field staff member received a report from a user and proceeded with immediate repairs. Another significant leak, estimated at 10 m³/hr, was detected during field inspection and promptly repaired. The remaining four locations require repairs to validate the project outcomes. Additional leaks caused by faulty angle valves on water meters were identified but were considered minor and thus not recorded.
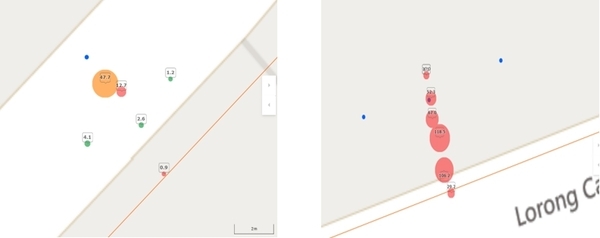
For areas requiring pinpointing, the Sonic GL_F logger was utilized to record data between 2 and 3 AM—when water usage by users is minimal—to identify leaks through correlation analysis.
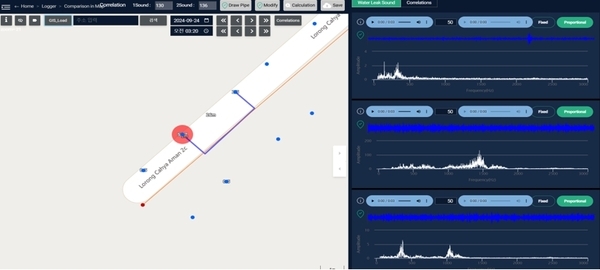

-
Pre-Pressure and Leak Noise Monitoring
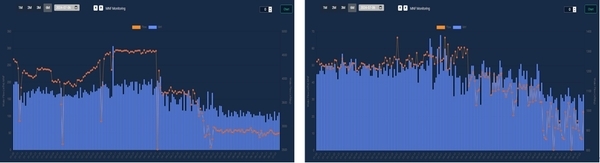
The Sonic M2_P remote pressure monitoring equipment, initially proposed by WI.Plat for cross-shaped installation, was instead installed at the pipeline endpoints per feedback from the local water authority (JBALB). The Sonic M2_L units were strategically placed at vulnerable points prone to leaks, such as the northern location (Lorong Cahya Mata) and areas within the Sub-DMA that have experienced significant leakage. Although there was some initial concern over installation methods for the Sonic M2_L, the prevalence of exposed pipes allowed for straightforward sensor attachment. Currently, data transmission is functioning smoothly, and WI.Plat is actively monitoring the data.


-
Flow Verification via Ultrasonic Flow Meters
To validate the project outcomes, ultrasonic flow meters were purchased and installed for two days each in the Main DMA and Sub-DMA areas. The primary goal is to measure the MNF reduction impact within the Main DMA. However, a leak of approximately 10 m³/hr was identified and repaired, prompting the installation of flow meters in the Sub-DMA to observe the correlation. Results showed a reduction in the inflow rate in the Sub-DMA from 19.7 m³/hr to 16.3 m³/hr—a decrease of about 17.3%. Flow measurements for the Main DMA will continue post-repair to verify project impact.

Lesson learned:
- Efficient System Implementation: The prompt adoption of the intelligent leak management system by local staff was instrumental in ensuring smooth operations from the outset. This highlights the importance of early, intensive training sessions to familiarize local personnel with new technologies. In this case, the familiarity of the NELOW system with easy-to-use features allowed for efficient integration and immediate functionality.
- Well-Structured Pipe Network Enhances Leak Detection: The pre-existing pipe network in Samariang was relatively well organized, which facilitated efficient leak detection and continuous monitoring. This experience suggests that areas with disorganized infrastructure might benefit from preliminary system optimization before the introduction of an intelligent management system
- Importance of Accurate and Modern Meters: The project revealed that aged and inaccurate water meters contribute significantly to non-revenue water (NRW). Regular and systematic replacement of aging water meters ensures better data accuracy and reduces NRW. It is essential for any NRW management plan to include a strategy for the ongoing replacement and calibration of water meters.
- Optimized Pressure Management: Pressure management was identified as a key factor in reducing water loss, particularly during low-demand nighttime hours. By optimizing night-time pressure, the water system can reduce stresses on the pipelines, leading to a decrease in leak formation and subsequently reducing NRW. This emphasizes the value of a pressure monitoring strategy as part of any comprehensive leak management system.
- Significance of Regular Leak Inspections: One of the critical findings from this project is the necessity for regular leak inspections to maintain an active leak management system. During the project, multiple leaks were identified and repaired, some of which were not previously noticeable without NELOW’s advanced monitoring capabilities. Continuous and systematic leak inspections, ideally conducted annually or even more frequently, are crucial for reducing water loss and ensuring system sustainability.
- Local Capacity Building and Technical Transfer: Capacity building for local staff was critical for the long-term sustainability of the project. Training provided to JBALB engineers on leak sound collection and remote monitoring device installation ensured that they could independently manage the system beyond the project period. This underscores the importance of thorough training and ongoing technical support in achieving lasting project outcomes.
- Stakeholder Engagement Is Key: Building relationships with key stakeholders, including local authorities and government agencies, was a critical enabler for project success. The CEO’s international experience and existing relationships facilitated smoother negotiations and ensured collaboration at different levels of government. Effective stakeholder management should therefore be prioritized in similar projects to align objectives and gain necessary support.